Vision for Introducing this Course
The CMA provides an invaluable understanding of finance that companies need to be efficient and profitable. CMAs often work closely with upper management, and their knowledge, skills, and experience influence the direction of these organizations. We focus on producing flawless Cost Accountants in every term ( June & December).
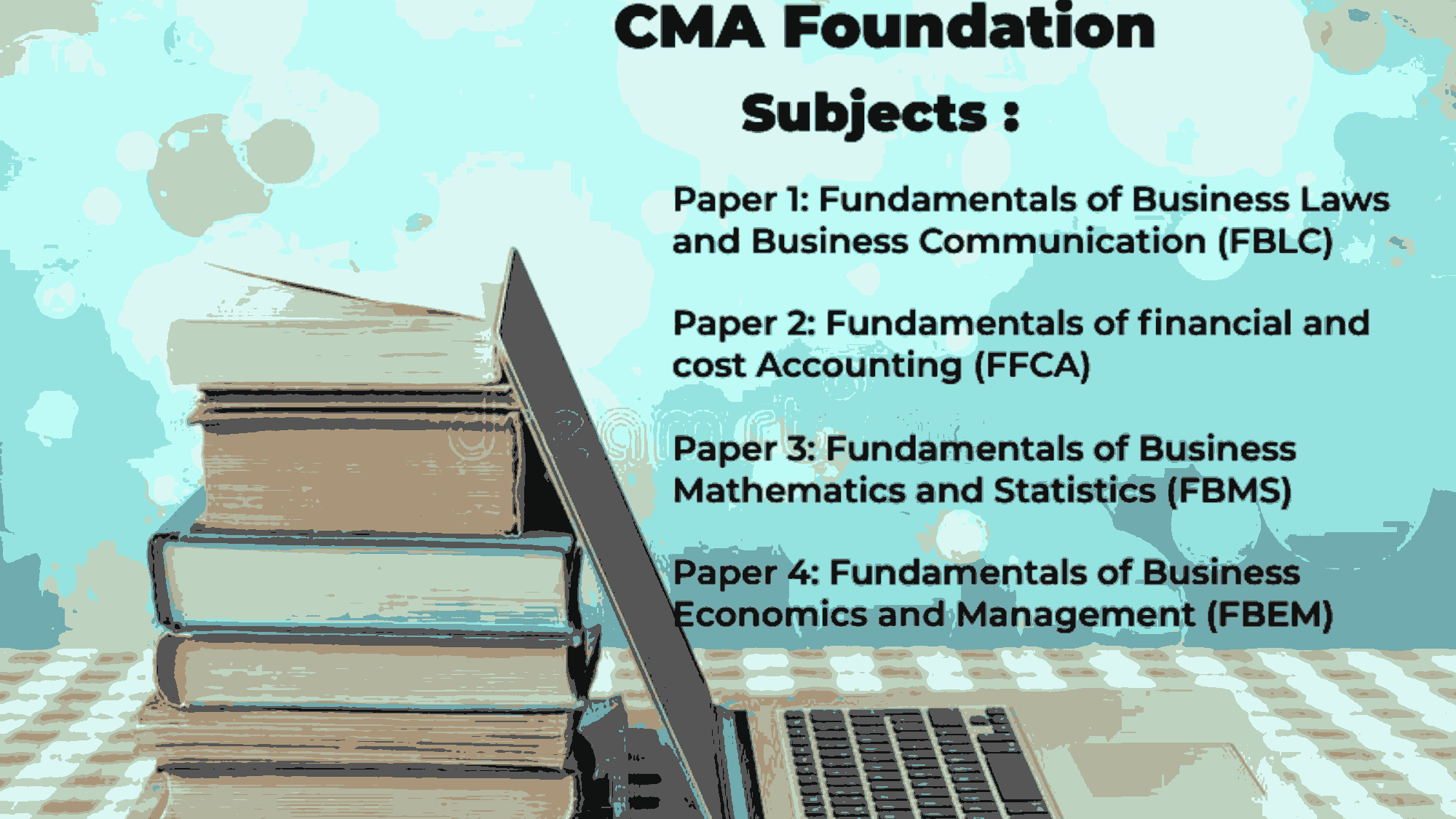
CMA foundation course is the first level to become a professional cost and management accountant. Students should take it seriously as it is not easy to pass this level. For the first time, the student is introduced to subjects like business laws & business communication , cost accounting, and management. Mathematics & statistics are also new subjects for the students who didn't opted Mathematics in +2 level. We have been an undoubted leader when it comes to converting young students into prudent professionals by providing educational facilities at the highest order. Classes are Conducted for English, & Hindi medium Students.
Subjects Offered: Principles and Practice of Accounting, Business Law and Business Correspondance and Reporting, Business Mathematics and logical Resoning & statistics, Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge.
| Subjects | Teachers |
|---|---|
| Principles and Practice of Accounting | CA Gayatri Sethy |
| Business Law and Business Correspondance and Reporting | CMA Ajay Deep Wadhwa |
| Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge | CMA Gour Bandhu Gupta |
| English | Anjana Gupta (M.A., English) (B.ED) |
| Business Mathematics and logical Resoning & statistics | CMA Gour Bandhu Gupta |
| Co-ordinator | CMA Manas Kumar Thakur |