Vision for Introducing this Course
This program is conducted as a comprehensive online course offered via online live interactive lecture sessions. We take special care not only of the mainstream subjects but also the reasoning and english portion. Different mechanism of approach has been adopted for multiple choice subjects(mathematics and economics) and subjective subjects (Accounts and law ). Classes are Conducted for English, & Hindi medium Students.
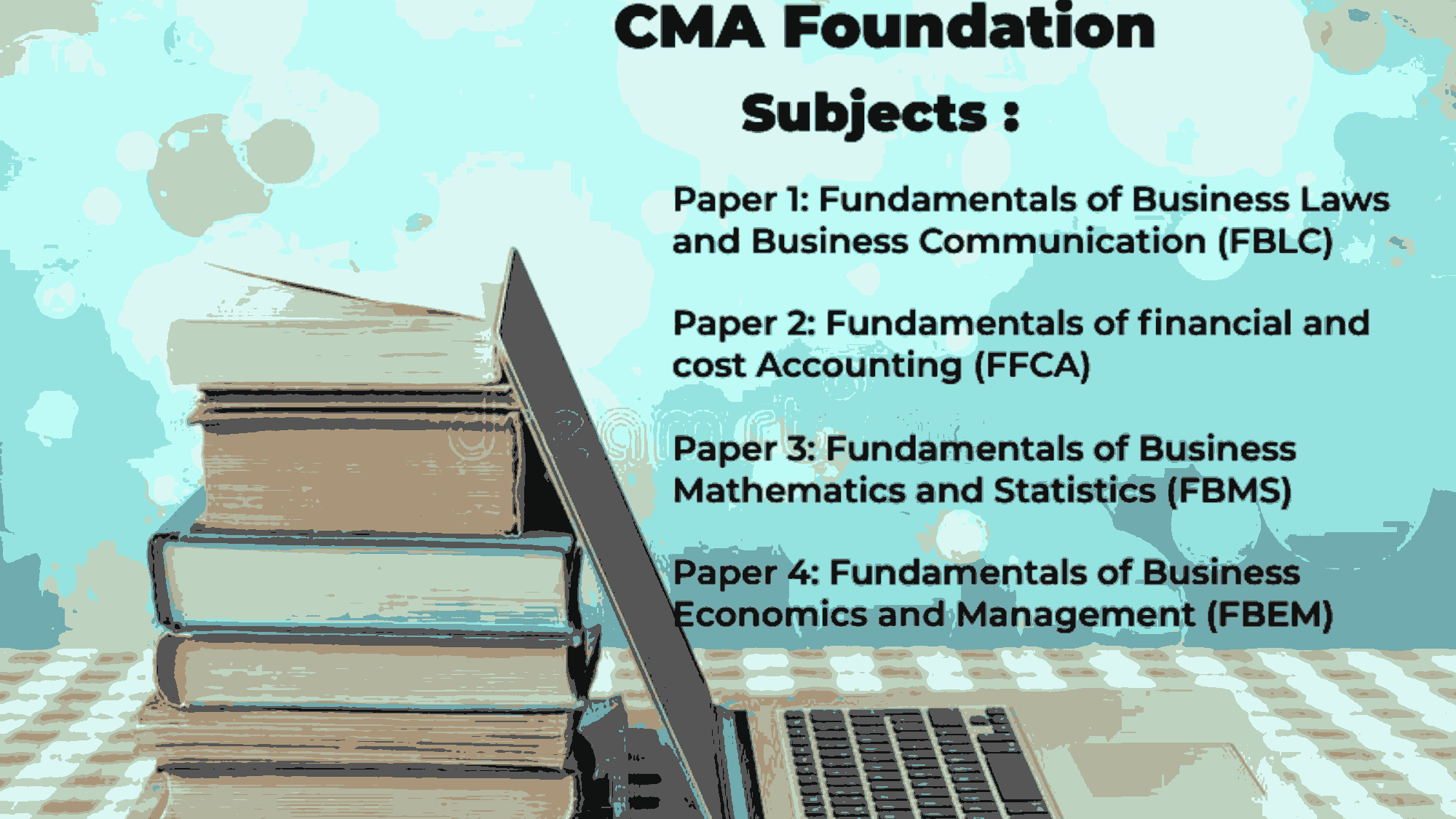
Subjects Offered: Principles and Practice of Accounting, Business Law and Business Correspondance and Reporting, Business Mathematics and logical Resoning & statistics, Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge.
| Subjects | Teachers |
|---|---|
| Principles and Practice of Accounting | CA Gayatri Sethy |
| Business Law and Business Correspondance and Reporting | CMA Ajay Deep Wadhwa |
| Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge | CMA Gour Bandhu Gupta |
| English | Anjana Gupta (M.A., English) (B.ED) |
| Business Mathematics and logical Resoning & statistics | CMA Gour Bandhu Gupta |
| Co-ordinator | CMA Manas Kumar Thakur |